TEL:+86 0536-6162866+86 187-6464-2379
ADD:No.19, Shunde Road, Zhucheng City, Shandong, China
WEB:www.uplee.com.cn
Egsb anaerobic reactor
-
MS:Katherine Wong
+86 187-6464-2379
-
TEL:+86 0536 6162866
MAIL:sales@cntianlang.com
-
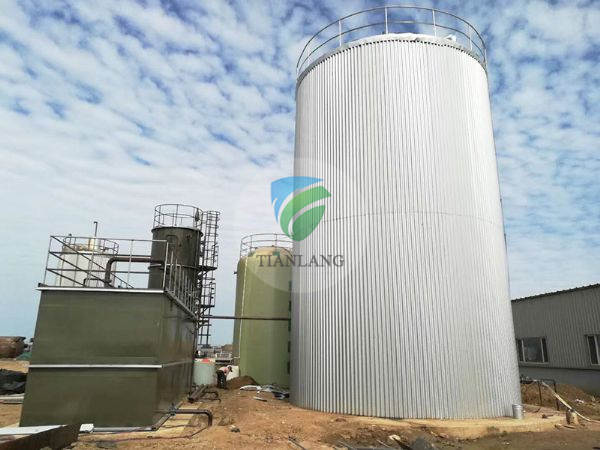


Product name:Egsb anaerobic reactor
Details
I. Introduction of EGSB reactor
EGSB is an expanded granular sludge bed reactor, which is a third-generation anaerobic reactor in which the granular sludge bed is partially or fully "expanded". To increase speed, the EGSB reactor uses a large height-to-diameter ratio and a large reflux ratio. At high speeds and agitation of the gas, the contact between the wastewater and the granular sludge is more sufficient. Due to good mixed mass transfer, all active bacteria in the EGSB reactor, including bacteria inside the granular sludge, can obtain organic matter from wastewater, that is, more microorganisms in the EGSB participate in the water treatment process. This allows the wastewater to have a short hydraulic retention time in the reactor.
Second, the EGSB reactor process principle
The anaerobic digestion process can be divided into four relatively independent but inseparable steps: the hydrolysis stage, the acidification stage, the hydrogen production acetogenic stage, and the methanogenesis stage.
A group of microorganisms, acidified bacteria, complete the first two steps of the anaerobic digestion process, hydrolysis and acidification. They hydrolyze polymers such as proteins, fats and carbohydrates into small molecules that can enter the interior of cells through extracellular enzymes, which are oxidatively degraded inside the cells to form carbon dioxide (CO2), hydrogen (H2) and major products - volatile fatty acids ( VFA).
The second group of microorganisms, the hydrogen producing acetogen, converts the above products into acetate, hydrogen and carbon dioxide during the acidification process.
The third group of microorganisms are methanogens that convert acetate or hydrogen and carbon dioxide to methane.
Third, EGSB reactor characteristics
1, BOD removal rate is high (90% ~ 95%); stable operation, simple structure.
2. It is easier to form granular sludge with uniform distribution, and the biomass in the sludge bed is large (up to 60g/l); it is very suitable for the treatment of medium and high concentration organic wastewater.
3, the volume load rate is high (20 ~ 30kgCOD / m3.d), the residence time is shorter, so the required volume is greatly reduced; the reactor volumetric load rate is more than 2-3 times higher than the ordinary UASB reactor.
4, easy to operate, using the method of swirling mixed water, uniform water distribution, good mass transfer, and there is no problem of blocking short flow.
5. An external reflux system is added. The alkalinity of the anaerobic reactor can be supplemented by reflux water, and the cost of lye can be greatly reduced.
6, high aspect ratio (generally 2-4), small footprint, easy to manage.
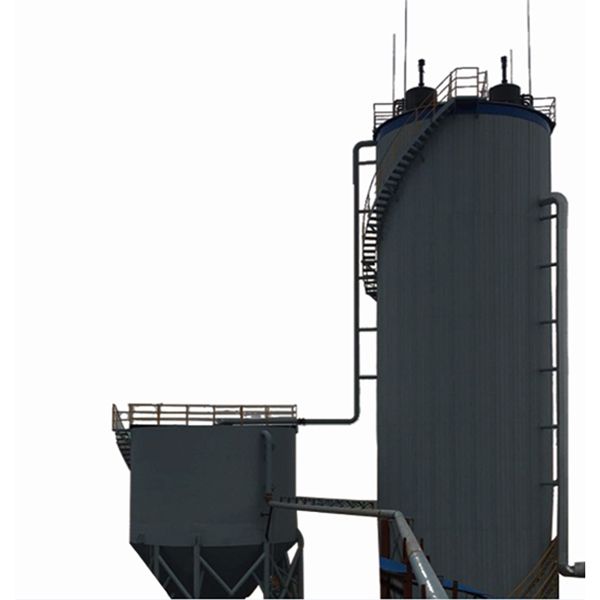






















 Tel
Tel Home
Home Products
Products