TEL:+86 0536-6162866+86 187-6464-2379
ADD:No.19, Shunde Road, Zhucheng City, Shandong, China
WEB:www.uplee.com.cn
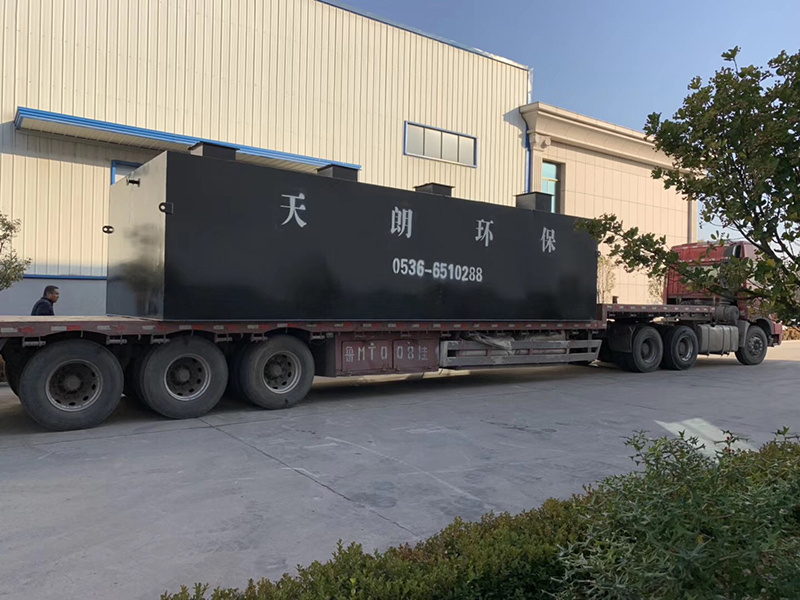
petroleum?sewage treatment plant
-
MS:Katherine Wong
+86 187-6464-2379
-
TEL:+86 0536 6162866
MAIL:sales@cntianlang.com
-
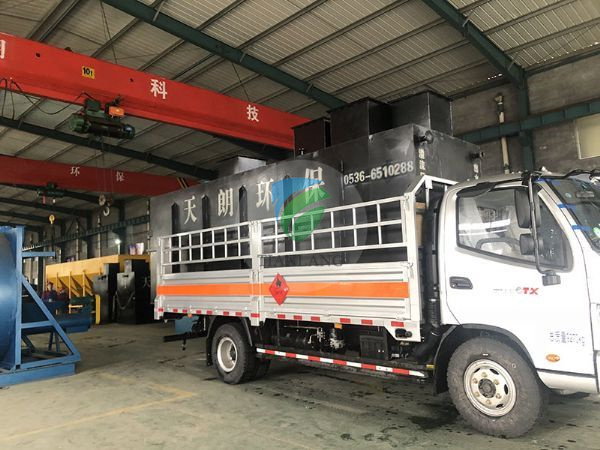


Name: petroleum sewage treatment plant
details
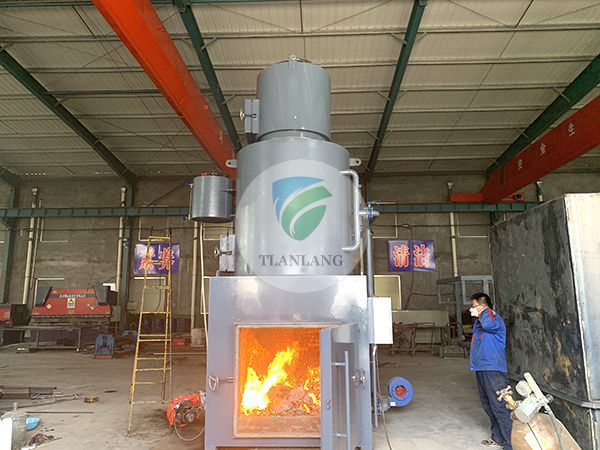
Note: The following are just a few common treatment methods. The specific processing method needs to be customized for you in combination with your situation. If you need detailed plans and quotations, please call our company service hotline, we have a dedicated technical staff to give you free programs and quotations.
The development of industry and the neglect of society by the environment have caused increasingly serious environmental pollution problems. For the treatment of toxic and difficult biodegradable organic wastewater, such as petroleum exploitation, pharmaceutical, pesticide, paper, printing and dyeing, there is still no economic and effective practical technology. These toxic, difficult to biodegrade substances are very harmful, and some are carcinogenic, teratogenic, and mutagenic. They pose a danger to biological life or human health through their own and their chemical composition. For example, the oil discharged into the water environment can prevent the oxygen in the air from dissolving into the water, causing the plankton in the water to die due to lack of oxygen, and causing the fish and shellfish to taste, unsuitable for consumption, and coalescing oil on the surface of the water body. It is also possible to burn and create safety problems. At present, most of China's oil fields have entered the middle and late stages of mining, and the water content of produced fluids has increased year by year, and many oil fields are above 90%. The petrochemical industry uses a combination of chemical and physical separations, using Yuanyou and natural gas as raw materials to process the required petroleum products, industrial raw materials and other products. The main pollutants are oil, sulfur, cyanide, phenol, suspended solids, as well as various organic substances and some heavy metals. If it is not treated and discharged into the receiving water body, it will cause serious pollution of water quality.
Petroleum exploration and development wastewater is divided into two types: petroleum exploration and development and petrochemical. According to different sources, petroleum exploration and development wastewater can be divided into oilfield production water, drilling sewage, well washing sewage and mining area rainwater.
The processing method has the following points:
(1) Physical law
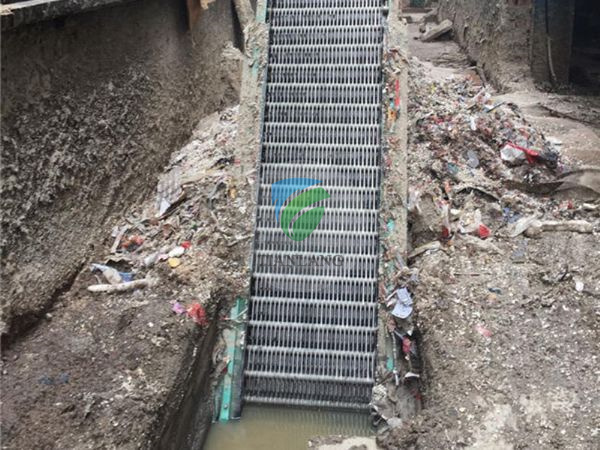
1. Grille: The grille should be installed at the wastewater inlet of the sewage treatment plant or in front of the sewage lift pump. Used to block coarse solids such as vegetation, garbage, plastics, fibers, etc., to prevent blockage or damage of pumps, pipes and subsequent equipment.
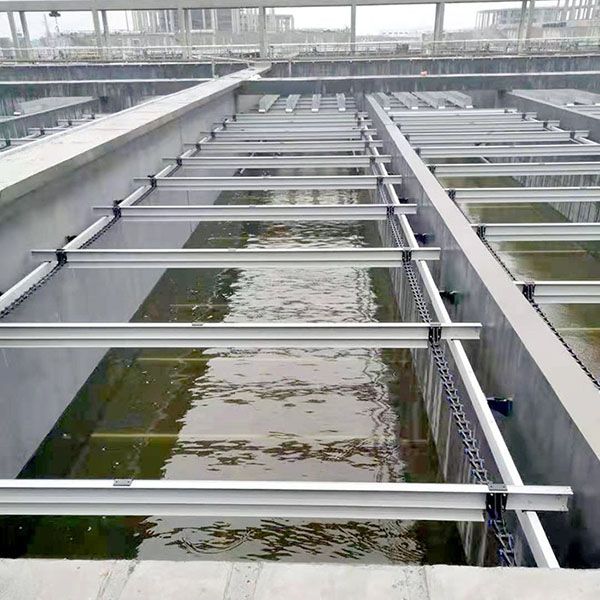
2. Precipitation: Sedimentation tanks are generally divided into advection, vertical, auxiliary flow and sloping plate sedimentation tanks. The primary sedimentation tank is a primary treatment, which is a pretreatment facility for biological treatment. Here, the main facility for sedimentation and separation of suspended solids in sewage is carried out. Oil companies often use sedimentation tanks or settling tanks to treat drilling and production wastewater to remove suspended solids. The secondary sedimentation tank is an indispensable structure for the biological treatment process and has been widely used in the sewage treatment plant of petrochemical enterprises. It is mainly used to remove sludge generated during biological treatment to obtain clarified treated water, while providing a certain concentration of return sludge for biological treatment equipment.
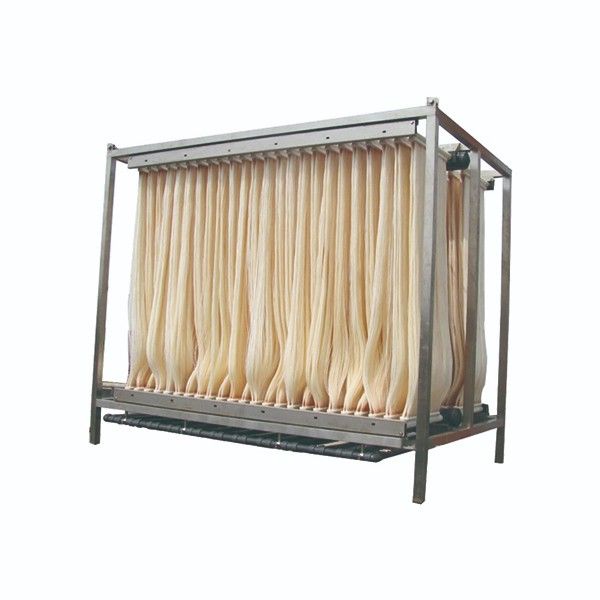
3. Oil-repellent: The oil-repellent treatment is mainly used to remove suspended and coarsely dispersed oil in oily sewage, so it is widely used in the petrochemical industry, especially in the treatment of oil production wastewater, the oil separation device is used as the core equipment. The oil separation device is generally divided into three types: flat flow type, swash plate type and flat flow swash plate combination type. The oil exploitation wastewater treatment generally adopts a grease trap, and the petrochemical wastewater treatment uses a grease trap.
4. Coalescence and oil extraction technology utilizes the difference between the oil-water two-phase properties and the disparity in the surface bonding force of the coalescing material. When the oily sewage passes through the bed filled with the coalescing material, the oil particles are used as materials. It is trapped and retained in the surface and voids of the material. As the oil particles are thickened to form an oil film, when the oil film reaches a certain thickness, a large oil bead is separated from the water. Coalescence and oil production has become an important technology for oil extraction wastewater treatment.
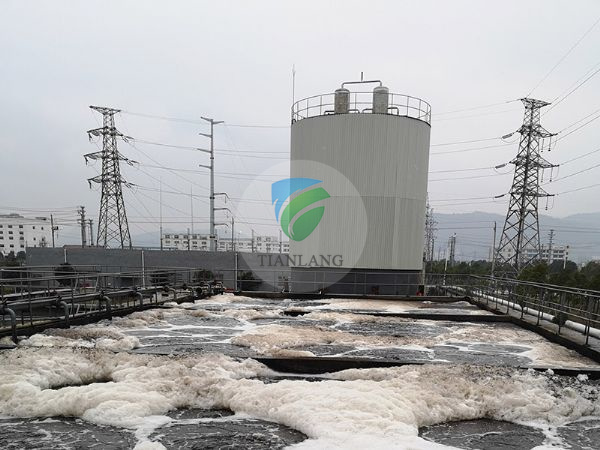
5. Suspension method, also known as air floatation method, works by trying to pass or generate a large number of bubbles in the water to form a three-phase non-uniform system of water, gas and removed substances, and the interfacial tension, buoyancy on the bubble and hydrostatic pressure difference. Under the action, the combination of bubbles and removed substances floats up to the surface of the water to achieve separation from water. Air floatation is commonly used in the petroleum and petrochemical industry to remove petroleum from water. The use of flotation agents is a simple and economical way to increase flotation efficiency. Originally used as a flotation agent, some inorganic flocculants such as AL2(SO4)3, basic ALCL3, and alum, which were later replaced by organic polymer flotation agents such as polyacrylamide, polyacrylic acid, starch, etc. .
6. Filtration is a process in which a granular filter material having a void, such as quartz sand or anthracite filter material, is used to intercept impurities in the water, thereby clarifying the water.
7. Extraction: In the mixture, the separation method between the components, in addition to the distillation method, can also be used for the extraction method. 8. Stripping: the acidic water discharged from the refinery production unit mainly contains NH3, H2S and CO2. If the water is directly discharged into the sewage treatment plant of the refinery, it will be treated according to the “old three sets” (oil separation, flotation, aeration) process, and the discharged wastewater will not meet the discharge standard. In order to ensure the smooth operation of the sewage treatment plant and the discharge of water, the pretreatment of the equipment must be carried out for wastewater containing sulfur and high ammonia nitrogen. By using the gas extraction method, the appropriate process and operating conditions can be used to purify the wastewater to various reclaimed water quality requirements or meet the requirements of the influent water quality indicators entering the sewage treatment plant, and can obtain by-products H2S and NH3 according to requirements. .
(2) Chemical law
1. Neutralization method: The so-called neutralization method is a method of adjusting the PH value of acid or alkali-containing wastewater to make it neutral, and some production facilities and auxiliary facilities of petrochemical plants are often discharged. Acid and alkali-containing wastewater, such as water washing of oil products, drainage of chemical facilities, washing water of oil tanks, treatment of boiler water, and drainage of acid-base pumping rooms. Under normal circumstances, the pH of alkaline wastewater is between 11-12, and the pH of acidic wastewater is 1-2. When using the neutralization method, appropriate acid-base agents should be added. Limestone, calcium carbide, NACO3 and other chemicals are commonly used in the treatment of acid waste water. When speculating limestone or gravel, the amount of sludge generated is large. Industrial sulfuric acid, hydrochloric acid, and nitric acid are required for the treatment of alkaline wastewater. It is more economical to use spent acid as a neutralizing agent.
2. Coagulation: In the water treatment, a coagulant is added to the water to destroy the stable state of the colloidal particles in the water. Under certain hydraulic conditions, the collision and aggregation between the colloidal particles and other particles are formed, thereby forming an easy Flocs separated in water, such as oil, fluid, arsenic, cadmium, surface active substances, radioactive materials, plankton and algae. The agent of the coagulation process can be divided into two major categories: coagulant and coagulant. Coagulants include two types, one is inorganic salts, such as polyaluminum chloride, and polyaluminum chloride is a high-molecular flocculant, such as polyacrylamide; coagulants include three types, one is acid-base, Such as limestone, etc., the second is flocculation cores, such as silica, activated carbon, various clays, precipitated sludge, etc., three are oxidants, such as chlorine, ozone and so on. The choice of coagulant, coagulant and other agents should be determined according to the process test of the treated water or with reference to the operating experience of similar treated water.
3. Oxidation: At present, in the wastewater treatment of the petrochemical industry, the air oxidation method is often used for the pretreatment of sulfide-containing materials, and the ozone oxidation method is used for the tertiary treatment of the discharged water to ensure that the discharge water reaches the standard.
(three), biochemical treatment
1. Wastewater anaerobic biological treatment
The anaerobic biological treatment method of sewage is also called "anaerobic digestion", which is a method for utilizing anaerobic microorganisms to degrade organic pollutants in sewage and purify the sewage. The mechanism is to decompose the organic matter in the sludge under the action of anaerobic bacteria, and then generate gases such as methane and carbon dioxide. The complete anaerobic digestion process can be divided into three stages: 1 The solid organic compound in the sludge is dissolved by the extracellular hydrolase secreted from the anaerobic bacteria, and enters the cell through the cell wall, and the polysaccharide is catalyzed by the hydrolase. , protein, fat are hydrolyzed into monosaccharides, amino acids, fatty acids, etc.; 2 under the action of acid-producing bacteria, the first-stage products are further degraded into simpler volatile organic acids, such as acetic acid, propionic acid, butyric acid; 3 Under the action of methanogens, the volatile acids produced in the second stage are converted into methane and carbon dioxide. Influencing factors include temperature, pH, nutrients, organic poisons, and anaerobic environments. Advantages of anaerobic biological treatment: less energy is consumed in the treatment process, high removal rate of organic matter, less sludge and easy dehydration, killing pathogenic bacteria, and no need to add nutrients such as nitrogen and phosphorus. However, anaerobic bacteria breed slowly, are sensitive to poisons, and require strict environmental conditions. The final product still requires aerobic biological treatment. In recent years, it is often used in biochemical treatment of high concentration organic wastewater.
2. Sewage aerobic biological treatment
The sewage aerobic biological treatment method is a sewage biochemical treatment method that utilizes aerobic microorganisms (mainly aerobic bacteria) to decompose organic pollutants in the sewage to make the sewage harmless. The mechanism is that when the sewage is in contact with the microorganism, the soluble organic matter in the water is absorbed into the bacteria through the cell wall and cell membrane of the bacteria; the colloid and the suspended organic matter are adsorbed on the surface of the bacteria, and are decomposed into the dissolved by the external enzyme of the bacteria. After the substance, it also enters the bacteria. These organic substances are oxidatively degraded by catabolic processes in the bacteria, and the energy generated is required for the life of the bacteria; part of the oxidized intermediates are anabolically metabolized into new cellular substances, allowing the bacteria to grow and reproduce. The final product of the treatment is a stable inorganic material such as carbon dioxide, water, ammonia, sulfate and phosphate. When processing, the microorganisms should be supplied with sufficient oxygen and various necessary nutrient sources such as carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus and elements such as potassium, magnesium, calcium, sulfur and sodium; and the living conditions of the microorganisms should be controlled, for example, the pH should be 6.5~ 9, the water temperature should be 10 ~ 35 ° C and so on. The main methods are active pollution method, biofilm method, oxidation pond method and the like.






















 Tel
Tel Home
Home Products
Products